Insights from Radiologists and Medical Specialists on Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) has emerged as a crucial medical procedure, offering a minimally invasive solution for various conditions. This innovative technique employs radiofrequency energy to heat and destroy targeted tissues, often replacing traditional surgical approaches. In this blog, we delve into the insights shared by radiologists and medical specialists regarding the utility, advancements, and challenges associated with radiofrequency ablation.
The Fundamentals of Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is based on the principle of using electrical currents to generate heat, which in turn obliterates abnormal or diseased tissues. Radiologists emphasize that the precision of this technique enables them to treat tumors, alleviate pain, and manage various medical conditions with fewer risks and complications compared to invasive surgeries.
Expanding Applications in Tumor Treatment
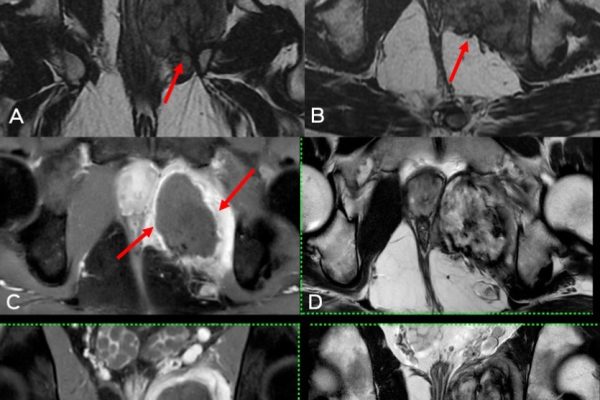
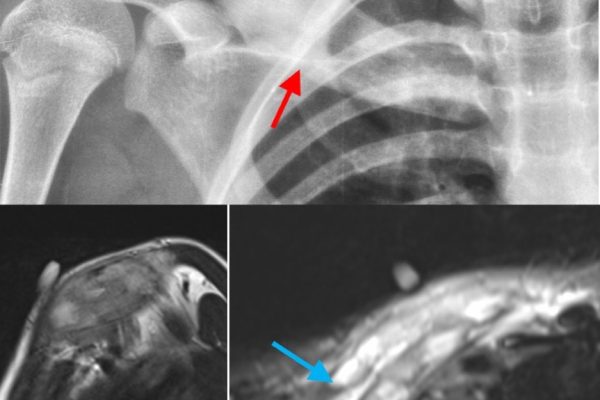
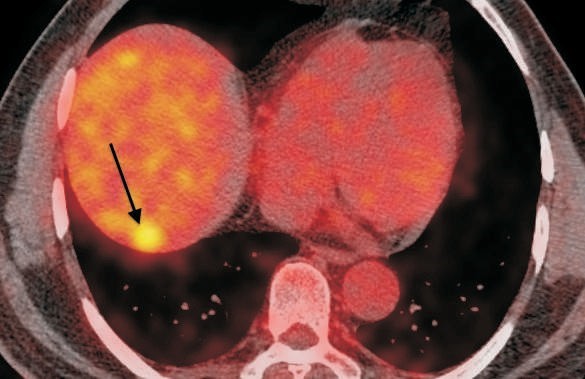
Medical specialists are increasingly turning to radiofrequency ablation for tumor treatment. Radiologists have found success in managing various types of tumors, including liver, kidney, lung, and bone tumors. They stress that radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is particularly effective for patients who are ineligible for surgery due to underlying health conditions or those who prefer a less invasive approach. Furthermore, the technique can often be repeated if necessary, allowing for ongoing tumor management.
Advantages Over Traditional Treatments
Radiologists highlight a number of benefits of radiofrequency ablation over traditional treatments. One major benefit is the reduced risk of complications and infection, as RFA doesn’t require large incisions. This translates to shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery time. Moreover, medical specialists highlight the preservation of healthy tissue, as RFA specifically targets abnormal cells, minimizing collateral damage.
Collaborative Approach for Optimal Outcomes
The success of radiofrequency ablation often relies on collaboration between radiologists, oncologists, and other medical specialists. These experts work together to identify suitable candidates for the procedure, determine the optimal approach, and ensure proper post-procedural care. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that patients receive comprehensive and personalized treatment plans.
Technological Innovations in RFA
Medical technology has rapidly advanced, and radiofrequency ablation techniques have evolved accordingly. Radiologists are excited about the development of real-time imaging techniques that allow them to precisely guide the RFA probe to the target area. Additionally, the integration of robotics and artificial intelligence has enabled greater accuracy and improved patient outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations
While radiofrequency ablation offers numerous benefits, medical specialists acknowledge that challenges do exist. For instance, the effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) can be limited in treating larger tumors or those located near critical structures. In such cases, alternative treatment options or a combination of therapies might be necessary. Additionally, the skill and experience of the radiologist performing the procedure play a significant role in its success.
Patient Selection and Education
Radiologists emphasize the significance of choosing the appropriate patients for radiofrequency ablation. Patient selection involves a comprehensive assessment of the tumor’s size, location, and characteristics. Moreover, medical specialists stress on the need for thorough patient education, ensuring that individuals understand the procedure, its benefits, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
The Future of RFA and Personalized Medicine
Looking ahead, both radiologists and medical specialists are optimistic about the future of radiofrequency ablation. They believe that ongoing research will refine the technique, broaden its applications, and lead to even better patient outcomes. With the advent of personalized medicine, RFA could be tailored to suit individual patient profiles, further enhancing its efficacy.
Conclusion
Radiofrequency ablation has revolutionized medical interventions by providing a minimally invasive solution for various conditions, particularly tumor treatment. The insights shared by radiologists and medical specialists highlight the tremendous potential of RFA in improving patient care, reducing risks, and enhancing recovery times. As technology continues to advance and interdisciplinary collaboration thrives, the future of radiofrequency ablation looks promising, offering hope to patients seeking effective and less invasive treatment options.